What C Word Defines A Substance That Speeds A Chemical Reaction Without Being Consumed
Tabular array of Contents
What is Reaction Rate?Factors Affecting the Charge per unit of ReactionRate of Reaction FormulaInstantaneous Rate of Reaction
The rate of reaction refers to the speed at which the products are formed from the reactants in a chemical reaction. It gives some insight into the time frame under which a reaction tin be completed. For example, the reaction rate of the combustion of cellulose in burn is very high and the reaction is completed in less than a second.
What is Reaction Charge per unit?
The rate of reaction or reaction rate is the speed at which reactants are converted into products. When we talk well-nigh chemical reactions, it is a given fact that rate at which they occur varies by a great deal. Some chemical reactions are nearly instantaneous, while others usually have some time to reach the final equilibrium.
This article aims to help students larn about and sympathise what exactly is the charge per unit of reaction for a given chemical chemical compound.
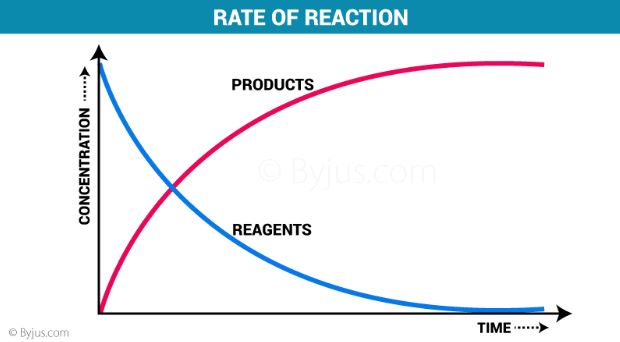
As per the full general definition, the speed with which a reaction takes place is referred to equally the charge per unit of a reaction.
For instance, wood combustion has a high reaction rate since the process is fast and rusting of iron has a depression reaction rate as the process is slow.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Reaction
The various factions that tin can bear on the rate of a chemical reaction are listed in this subsection.
Nature of the reaction
- The rate of reaction highly depends on the type and nature of the reaction. As mentioned earlier, few reactions are naturally faster than others while some reactions are very ho-hum.
- The physical country of reactants, number of reactants, complication of reaction and other factors highly influence the reaction rate too.
- The rate of reaction is mostly slower in liquids when compared to gases and slower in solids when compared to liquids. Size of the reactant likewise matters a lot. The smaller the size of reactant, the faster the reaction.
Upshot of concentration on reaction rate
- According to the collision theory, the charge per unit of reaction increases with the increment in the concentration of the reactants.
- Every bit per the police of mass activity, the chemical reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants.
- This implies that the chemical reaction rate increases with the increase in concentration and decreases with the decrease in the concentration of reactants.
- Time plays a major role in irresolute the concentration of reactants and products. Therefore, even fourth dimension is a vital factor affecting the reaction rate.
Recommended Videos

Pressure level gene
- Pressure increases the concentration of gases which in turn results in the increase of the rate of reaction. The reaction rate increases in the direction of less gaseous molecules and decreases in the reverse management.
- Thus, it tin can be understood that pressure and concentration are interlinked and that they both affect the rate of reaction.
How does temperature touch on the reaction rate?
- Co-ordinate to collision theory, a chemical reaction that takes identify at a college temperature generates more free energy than a reaction at a lower temperature.
- This is because colliding particles will accept the required activation energy at high temperature and more than successful collisions volition take place.
- There are some reactions that are independent of temperature. Reactions without an activation bulwark are examples of chemic reactions that are contained of temperature.
Solvent
The rate of reaction also depends on the type of solvent. Backdrop of solvent and ionic force highly bear upon the reaction rate.
Order
The lodge of reaction manages how the reactant pressure or concentration affects the rate of reaction.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy and its presence at the chemic reaction may increase the rate of reaction equally it gives the particles of reactants more than energy.
Intensity of Lite
Fifty-fifty the intensity of light affects the charge per unit of reaction. Particles blot more energy with the increase in the intensity of low-cal thereby increasing the rate of reaction.
Presence of Catalyst
- A goad can be defined as a substance that increases the rate of the reaction without actually participating in the reaction. The definition itself describes its effect on chemical reactions.
- The presence of a catalyst increases the speed of reaction in both forward and reverse reaction by providing an alternate pathway which has lower activation energy.
Surface Area of the Reactants
The surface expanse of reactants affects the charge per unit of reaction. If the size of a particle is small, the expanse volition exist more than and this increases the speed of heterogeneous chemical reactions.
Rate of Reaction Formula
Let'southward take a traditional chemical reaction.
a A + b B → p P + q Q
Capital letters (A&B) denote reactants and the (P&Q) denote products, while small-scale letters (a,b,p,q) denote Stoichiometric coefficients.
As per IUPAC'southward Gold Book, the charge per unit of reaction r occurring in a airtight organisation without the germination of reaction intermediates under isochoric conditions is defined equally:

Here, the negative sign is used to bespeak the decreasing concentration of the reactant.
Average Rate of reaction
Now let united states of america consider the following reaction to empathise fifty-fifty more conspicuously.
A → B
In this reaction a reactant A undergoes a chemical reaction to requite a production B. It is a full general convention to represent the concentration of whatsoever reactant or product every bit [reactant] or [product]. So the concentration of A can be represented as [A] and that of B as [B]. Let the fourth dimension at which the reaction begins be the start time, that is t=0.
Allow'southward consider the following situation:
At t=t1,
The concentration of A=[A]1
The Concentration of B=[B]1
At t=tii,
The concentration of A=[A]ii
The concentration of B=[B]ii
Now we want to know the rate at which A (reactant) is disappearing and the charge per unit at which the product B is appearing in the time interval between t1 and t2. Therefore,
The rate of Disappearance of A =
\(\begin{assortment}{50}\frac{[A]_{2} – [A]_{1}]}{t_{ii} – t_{ane}} = – \frac{\Delta [A]}{\Delta t}\terminate{array} \)
The negative sign shows that the concentration of A is decreasing.
Similarly,
Rate of disappearance of B =
\(\begin{array}{50}\frac{[B]_{2} – [B]_{1}]}{t_{2} – t_{ane}} = \frac{\Delta [B]}{\Delta t}\end{array} \)
Since A is the simply reactant involved in the reaction and B is the only product that is formed and every bit mass is conserved, the corporeality of A disappeared in the time interval Δt will be aforementioned as the corporeality of B formed during the same time interval. Then we can say that
The rate of reaction = – Charge per unit of disappearance of A = Rate of appearance of B
Therefore, Charge per unit of Reaction =
\(\begin{assortment}{l}- \frac{\Delta [A]}{\Delta t} = \frac{\Delta [B]}{\Delta t}\end{array} \)
The above terms for the rate of disappearance of A and rate of appearance of B are boilerplate rates of reaction. These rates give the rate of reaction for the unabridged fourth dimension interval Δt and hence are chosen average rates of reaction.
Instantaneous Rate of Reaction
What if we want to know the rate at which the reaction discussed above is proceeding at whatsoever instant of time and non for a given menses of time? The average reaction rate remains abiding for a given time period and so it can certainly not give any idea well-nigh the rate of reaction at a particular instant.
This is where the instantaneous charge per unit of reaction comes into the picture. Instantaneous charge per unit of reaction is the rate at which the reaction is proceeding at whatsoever given time.
Suppose the value of the term Δt is very small and tends to nada. Now, we have an infinitesimally modest Δt which is a very small fourth dimension period and tin can be considered a particular instant of fourth dimension. The average reaction rate will exist the instantaneous rate of reaction.
Mathematically,
Average Charge per unit of Reaction =
\(\brainstorm{array}{50}- \frac{\Delta [A]}{\Delta t} = \frac{\Delta [B]}{\Delta t}\end{array} \)
When Δt →0
Instantaneous Rate of Reaction =
\(\begin{assortment}{l}- \frac{\Delta [A]}{dt} = \frac{\Delta [B]}{dt}\terminate{assortment} \)
Instantaneous Rate of Reaction =
\(\begin{array}{l}- \frac{d[A]}{dt} = \frac{d[B]}{dt}\cease{array} \)
The unit of measurement of charge per unit of reaction is given past concentration/time that is (mol/L)/sec.
Meanwhile, chemical kinetics has gained a critically significant part in the world today. The reaction rate (both average and instantaneous) is enabling engineers and scientists effectually the globe to optimize the process parameters in guild to get the most desired results from a chemic reaction in the most economical and safe fashion.
Chemical kinetics along with its critical office in the manufacturing manufacture has besides served as a base for further advances in the fields of reaction engineering science and biochemical engineering.
Whatsoever chemical reaction contains the following two constituents
- Reactants
- Products
The part these constituents play in chemical reactions is briefly described beneath. Of import concepts in chemical reactions such as activation energy are also described.
Reactants
Substances which undergo chemical reactions are called reactants. In a chemical reaction, these reactants are converted into new substances.
Products
The substances which are the stop products of a chemical reaction are called products. In other words, new substances that are formed due to the chemical reactions are all called products.
Activation Free energy
Activation energy can be defined as the minimum amount of free energy that is required to actuate molecules or atoms and then that they can undergo chemical transformation. This minimum energy is to overcome the energy barrier is called activation free energy.
Similarly, chemical kinetics is a part of concrete chemical science that is related to the report of reaction rates. It has many applications that include enzymology, chemical engineering, and environmental engineering.
In a chemical reaction, products are formed due to the collision between the reactant molecules.
The conditions for the collisions to form products are:
- Collisions should be effective.
- The right orientation of reactant molecules towards each other.
- All molecules should possess a minimum amount of free energy to form product molecules.
Equally the chemical reaction advances, the concentration of reactants will decrease and the concentration of products will increase.
To learn more, register with BYJU'Due south and download our app.
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/rate-of-reaction/
Posted by: mcmichaelnothessim64.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What C Word Defines A Substance That Speeds A Chemical Reaction Without Being Consumed"
Post a Comment